How AI in Patient Recruitment Cuts Trial Timeline?
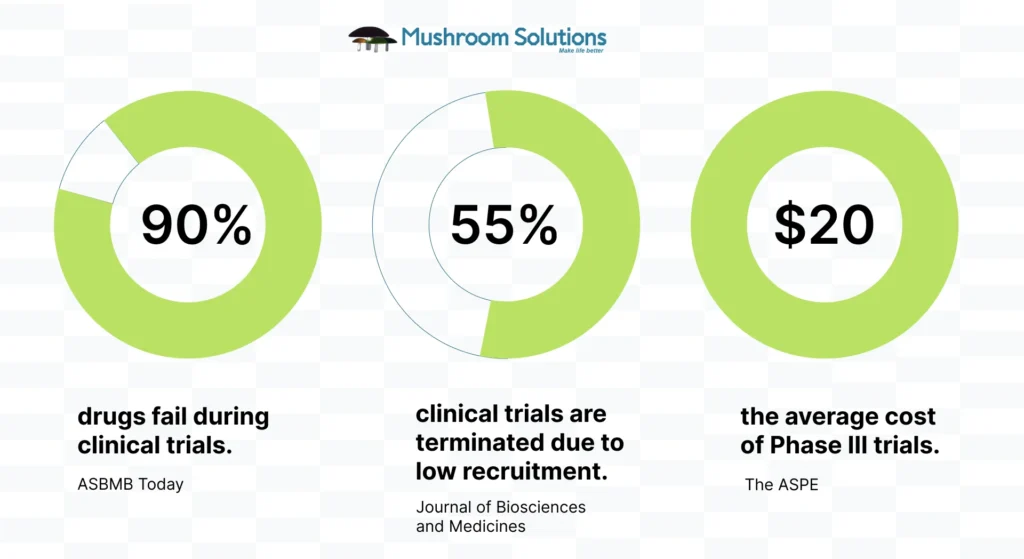
According to a Tufts CSDD report nearly 80% of clinical trials fail to meet enrollment timelines. Can AI (Artificial Intelligence) in patient recruitment be a game-changer in identifying eligible candidates faster, improve diversity, and reduce dropout rates? This blog explores the challenges of traditional recruitment and the AI-solutions in offer.
Persistent Challenges in Patient Recruitment
Despite being one of the most critical phases of clinical research, patient recruitment remains one of the most persistent bottlenecks in the drug development process. Delays in enrollment can derail study timelines, inflate costs, and sometimes result in trial termination altogether.
These delays have real-world consequences, not just for pharmaceutical companies and CROs, but for patients waiting on breakthrough therapies. Inadequate recruitment also leads to underpowered studies, poor population representation, and ultimately, compromised outcomes.
1. Overestimated Eligible Patient Population
Protocol feasibility assessments often misjudge the size of the actual eligible population. Factors like stringent inclusion/exclusion criteria and comorbidity restrictions can drastically reduce the cohort of qualified candidates, leading to under-enrollment and trial delays.
2. Lack of Awareness and Understanding Among Patients
Many potential participants are unaware that clinical trials are even an option. Limited outreach, poor patient education, and mistrust—especially among underserved communities—further widen the awareness gap, resulting in low engagement and response rates.
3. Logistical Barriers to Trial Participation
Location constraints, travel time, and scheduling conflicts present significant hurdles, especially for patients in rural or underserved regions. These logistical challenges often deter participation even when interest exists.
4. Participant Burden and Retention Challenges
Even when patients enroll, high dropout rates remain a concern. Time-consuming visits, invasive procedures, complex instructions, and insufficient follow-up support contribute to participant fatigue and attrition.
5. Competition Among Concurrent Trials
In high-demand therapeutic areas, multiple studies often compete for the same patient population. This saturation makes recruitment more difficult and increases the pressure on sites to differentiate their trial protocols and outreach efforts.
6. Recruitment Funnel and Attrition Across Trial Phases
From initial outreach to randomization, each phase of the recruitment funnel sees a significant drop-off. Screening failures, consent withdrawals, and logistical dropouts reduce the effective enrollment pool, making early-stage recruitment efficiency critical.
7. Therapeutic Area-Specific Challenges
Recruitment is particularly difficult in certain domains:
- Oncology: Patients are often in advanced disease stages with limited time to consider trial participation.
- CNS Disorders: Cognitive impairment and stigma complicate recruitment and informed consent.
- Cardiovascular Trials: High comorbidity rates and complex medication regimens often disqualify otherwise willing participants.
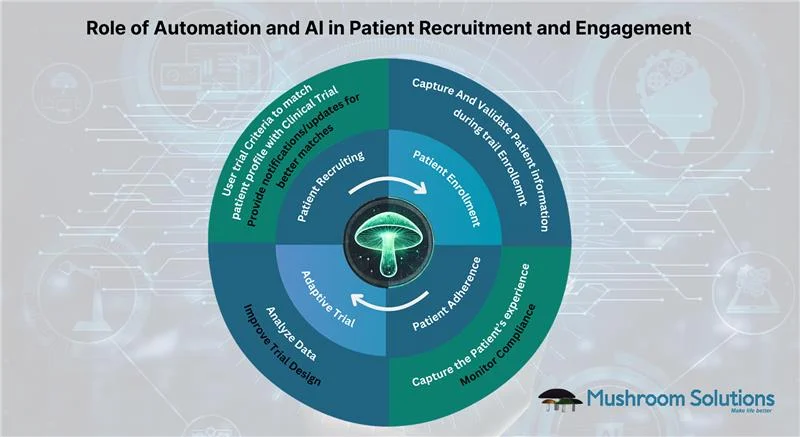
AI-Enabled Solutions to Enhance Patient Recruitment
AI is rapidly transforming patient recruitment by introducing speed, precision, and scalability into what has traditionally been a labor-intensive and unpredictable process. From pre-screening to personalized outreach, AI technologies are helping sponsors and sites overcome persistent recruitment hurdles.
Automating Eligibility Evaluation
Manual eligibility assessments are time-consuming and error-prone, often requiring staff to parse complex medical histories and trial protocols. AI models—especially those using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML)—can rapidly analyze electronic health records (EHRs), lab results, and unstructured clinical notes to identify qualified candidates with remarkable accuracy. Unlike traditional systems that rely on keyword matching, NLP models understand clinical context. Generative AI models match patient data with trial eligibility criteria in seconds, enabling real-time pre-screening at scale and freeing up site resources.
Reducing Screening Burden on Sites
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle early-stage patient engagement, answering common questions, collecting consent, and guiding individuals through eligibility assessments—before a human coordinator ever gets involved. This not only optimizes the patient enrollment process but also improves the patient’s experience. Conversational AI can be leveraged to pre-screen participants and handle a wide range of early-stage recruitment tasks:
- Answering common patient questions
- Conducting consent pre-checks via eConsent
- Guiding individuals through triage questions
- Providing trial information in simplified language
- Language personalization for global trials
These intelligent interfaces improve both patient experience and operational efficiency, allowing human coordinators to focus on high-touch activities. In addition, they help maintain engagement throughout the recruitment funnel, keeping prospective participants informed and motivated.
Predicting Dropouts and Mitigating Delays
Recruitment is only the first half of the challenge—retaining participants is equally crucial. ML models, trained on historical trial data, can identify patterns that correlate with patient dropout risks such as:
- Missed visits
- Non-Adherence to Medication
- Response delays or reported side effects
- Psychosocial variables
These early-warning insights empower sites to take proactive actions—like sending personalized nudges, adjusting protocols, or offering extra support—to improve retention and minimize costly trial delays.
Driving Diversity and Inclusion
Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA now emphasize the importance of demographic representativeness in clinical trials. AI tools can analyze large, heterogeneous datasets—spanning EHRs, claims data, and social determinants of health—to identify underrepresented populations and guide inclusive recruitment strategies.
These models help ensure that trials reflect real-world patient populations, strengthening the external validity of findings and supporting regulatory compliance. AI-powered chatbots, like MbotF, enable remote patient participation and alleviate the need for frequent site visits. This drives lower dropout rates, increased diversity and supports decentralized trials.
A compelling example of this technological advancement emerged during a Phase III cytokine storm study conducted amid the COVID-19 crisis. When traditional recruitment methods fell short, researchers deployed an innovative geofencing approach powered by AI and ML algorithms. The strategy focused on creating highly targeted campaigns within specific geographic zones surrounding participating research centers.
Through continuous analysis of location analytics, demographic patterns, and digital engagement behaviors, the initiative delivered exceptional results. The location-based targeting generated more than 17,000 unique weekly visitors to the study’s enrollment portal. This digital traffic translated into 460 qualified prospects, achieving a remarkable 7% conversion rate from initial web engagement to secondary screening—a performance metric that exceeded standard industry benchmarks by 50%.
Personalized Awareness and Outreach
Traditional mass outreach campaigns are being replaced by intelligent, data-driven targeting. AI can segment potential participants based on clinical, behavioral, and psychographic data, enabling sponsors to deliver highly personalized content across channels patients actually use.
Multimedia formats—videos, infographics, chat-based content—can be adapted dynamically for different platforms (e.g., Facebook, YouTube, patient portals), improving engagement and conversion rates. Gen AI plays a key role in the creation of patient awareness materials.
Remote Monitoring & Retention Support
AI-powered wearables and sensors enable real-time, continuous monitoring of participant health without frequent clinic visits. This not only enhances data quality but also reduces participant burden, making trial involvement more convenient.
AI also enables proactive retention strategies through:
- Multilingual chatbot engagement
- Personalized reminders and encouragement
- Adaptive interventions for at-risk participants
These tools transform the trial experience from transactional to supportive, improving patient satisfaction and study completion rates.

A Case Study of AI-Powered Intelligent Automation Solutions for Patient Recruitment
Consider this Intelligent Automation system that utilizes multiple AI technologies to streamline patient recruitment for clinical trials. Data from electronic medical records—including medical history, imaging , and laboratory findings—can be processed using document analysis and ML tools such as DocuGenX.
Through rule-based matching, this extracted data is compared against study eligibility criteria to determine optimal candidate selection. The system generates a prioritized list of suitable clinical trials for each patient, considering factors like treatment protocols, geographic proximity, and study timeline.
Using robotic process automation technology, automated alerts are transmitted via CTMS (Clinical Trial Management Systems), provider messaging platforms, or mobile applications to notify healthcare professionals about promising trial matches. Patients can also receive this information directly through their patient portal.
Following collaborative review of these recommendations, physicians can proceed with patient registration for the most appropriate trial option. This complete workflow can be coordinated through clinical trial management systems like CTOps, ultimately reducing trial failures caused by insufficient participant enrollment and accelerating trial outcome.
Challenges of Using AI in Clinical Trials—and How to Overcome Them
While AI offers groundbreaking potential in patient recruitment and retention, its adoption comes with a unique set of challenges. For AI to truly revolutionize clinical trials, stakeholders must navigate these hurdles with strategic foresight.
Data Quality & Bias
AI is only as good as the data it learns from. Inconsistent, incomplete, or biased data can skew outcomes, potentially exclude eligible patients or produce unfair recommendations.
Solution: Implement robust data validation processes and train AI models on diverse, representative datasets to ensure accurate and equitable results. Check consistency and track origin of data with Data Lineage tools and validate.
Interpretability & Trust
AI models—especially deep learning algorithms—can function as “black boxes,” producing decisions that are difficult to explain or justify. This lack of transparency can be a major barrier in a field built on trust and regulatory scrutiny.
Solution: Leverage explainable AI (XAI) frameworks and provide clear documentation of how algorithms make decisions to build confidence among researchers and regulators.
Model Degradation Over Time
In dynamic environments, AI models can degrade as new data enters the system, reducing accuracy and relevance. This is particularly critical in trials that span months or years.
Solution: Set up continuous performance monitoring and regularly retrain models to adapt to evolving datasets and clinical contexts.
Data Privacy & Security
AI systems often require access to large volumes of sensitive patient data, raising the stakes for privacy and security breaches.
Solution: Employ end-to-end encryption, secure data storage, and strict access controls. Leverage PII Redaction tools to hide sensitive personal information from EMR. Ensure full compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and other local data protection standards.
Overreliance on Technology
There’s a growing concern that AI may overshadow human judgment, leading to over-dependence and skill erosion among clinical professionals.
Solution: Position AI as an augmentation—not replacement—of human expertise. Provide continuous training to empower professionals to work alongside AI tools effectively and ethically.
From Smarter Recruitment to Faster Trial Outcomes: The AI Advantage
AI is not just optimizing workflows—it’s redefining the patient recruitment and retention paradigm. With its ability to automate, personalize, and predict, AI is helping sponsors and sites reach the right patients faster, support them more effectively, and deliver better outcomes with greater efficiency.
In this new era of intelligent trials, AI isn’t just a tool—it’s a strategic partner in accelerating clinical trials while putting the patient’s experience front and center.
Accelerate Patient Recruitment with AI—Today
Whether you’re looking to integrate AI-driven pre-screening, deploy intelligent chatbots, or enable predictive analytics for retention—we can help.


